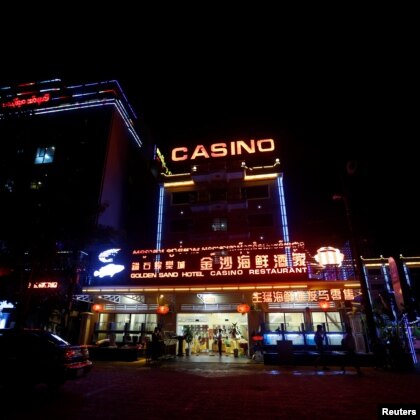
Local Cambodians worry about the influx of Chinese businesses such as this restaurant, hotel and casino in Preah Sihanoukville province. (Samrang Pring | Reuters)
Community Stories
Friends with Benefits
For Cambodia’s prime minister of more than three decades, a blossoming alliance with China means no Western powers questioning his increasingly authoritarian rule. For China, Cambodia offers a regional voice of support for its controversial expansion in the South China Sea.
For a more than 25 years, the West has helped rebuild Cambodia as it recovered from the genocidal Khmer Rouge regime. The United States and Europe sent billions of dollars in aid to help transform Cambodia into a liberal democracy, an effort that has largely failed.
Cambodia is now the one country in Southeast Asia openly embracing China. Hun Sen, the prime minister who has ruled Cambodia for more than three decades, has taken a strong anti-American line in a tense run-up to July’s election, and the surge in China’s economic and political influence mirrors a downturn in relations with the United States and the European Union over deteriorating human rights and political freedoms in the country.
“Chinese investment and diplomatic backing have become vitally important for Hun Sen’s rule, as he seeks freedom from the democratic demands of the West,” said Sebastian Strangio, author of “Hun Sen’s Cambodia.” “The Cambodian government, therefore, has good reasons to downplay the negative effects of Chinese investments while emphasizing the positives.”

Cambodian Prime Minister Hun Sen, right, talks with Xiong Bo, China’s ambassador to Cambodia, front left, during the inauguration ceremony for a sky bridge funded by China in Phnom Penh, Cambodia, July 2, 2018. (Heng Sinith | AP)
Last November, Cambodia’s Supreme Court dissolved the main opposition voice, the Cambodia National Rescue Party (CNRP). Hun Sen accused Washington of backing a plot led by CNRP to overthrow him during the 2013 election. The allegations were used to dissolve the party and jail its leader Kem Sokha, who had been in pre-trial detention since his arrest in September on charges of “treason” for colluding with foreign governments to bring about the overthrow of Hun Sen. Kem Sokha, his lawyer and most of the international community have called the charges baseless.
As a result of the CNRP’s dissolution, the White House ended its support for Cambodia’s National Election Committee (NEC), doubting the election’s validity. The European Union followed. China stepped in to donate $20 million to the NEC, said Hang Puthea, a spokesman for the body.
On May 15, the Committee for Free and Fair Election (COMFREL) an NGO respected for its election monitoring announced its withdrawal from monitoring the July election, claiming pressure from the government.
In June, NEC confirmed that China is one of the three countries with Myanmar and Singapore, sending election observers to monitor the vote.
“National Election of Cambodia (NEC) has officially been approved for 50,000 international and national electoral observers from 82 institutes including international observers from Myanmar, China and Singapore,” NEC’s statement said.
Kang Savang, a country coordinator for COMFREL, told VOA Khmer that he questions how electoral monitors from undemocratic countries will be able to assist in a free and fair election.
“Some counties have no experience in elections, but are monitoring Cambodia’s election? And, they will be evaluating Cambodia’s election outcome?” Kang Savang said.
Ear Sophal, associate professor of Diplomacy and World Affairs at Occidental College in Los Angeles and a co-author of “The Hungry Dragon: How China’s Resource Quest is Reshaping the World,” told VOA Khmer via email that China is not an objective election observer.
“Fake democracies encouraging other fake democracies equals the people los[ing],” Ear Sophal said. “It’s not a good sign for either [Cambodian democracy or the ruling party]. It shows the insecurity of the ruling party, which never before had to resort to such tactics.”
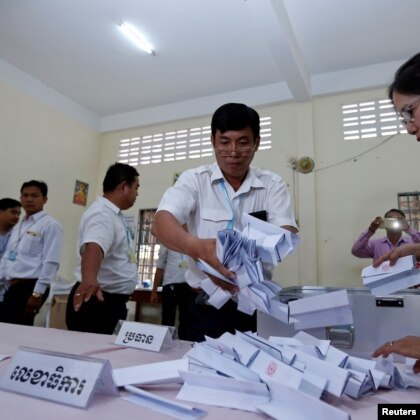

Members of Cambodia’s National Election Committee count ballots during a Feb. 25 Senate election in Phnom Penh. The committee was among the targets of a recent cyberattack, which a U.S. cybersecurity firm believes was engineered by the Chinese government. (Reuters)
Then, on July 10, the U.S. cybersecurity firm FireEye Inc. issued a report saying that hackers affiliated with Beijing had breached the computer systems of Cambodia’s key institutions.
While FireEye did not find evidence that Chinese hackers are working to influence the virtually uncontested Cambodian elections, the firm stated: “We expect this activity to provide the Chinese government with widespread visibility into Cambodian elections and government operations.” The Foreign Ministry in China has rejected the allegations.
In an email to VOA Khmer, Ear Sophal wrote, “The Chinese want to make money and have strategic influence in Cambodia. They only lose if the ruling party and its chief don’t stay in power.”)
From politics to direct investment
In Cambodia, Beijing has a friend willing to support its claims to the South China Sea. As friends do, China marked that favor with gifts — political support for Hun Sen, infrastructure loans and investments. And as Cambodia continues to move away from the West, China’s economic influence is growing. China is the biggest investor in Cambodia, accounting for up to 44 percent of the $19.2 billion in foreign direct investment (FDI) between 1994 and 2014, according to the National Bank of Cambodia (NBC) and the National Institute of Statistics (NIS).
China also supports Cambodia’s tourist industry. Some 1.2 million Chinese citizens visited Cambodia last year, a figure that is expected to rise to nearly 2 million by 2020.
According to the finance ministry, Cambodia owes China more than $4 billion, or about two-fifths of the country’s outstanding debt. The figure is significantly higher than the combined multilateral debt owed to institutions such as the World Bank and Asian Development Bank.
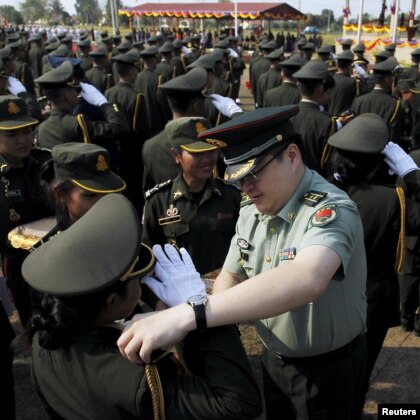

A Chinese army advisor awards rank insignia to Cambodian army graduates during a 2015 ceremony in Kampong Speu province. Military aid has strengthened China's ties with Cambodia, and analysts see it as part of Beijing’s push to extend its regional influence. (Samrang Pring | Reuters)
Military cooperation
In June, during an official visit, Chinese Defense Minister Wei Fenghe pledged nearly $100 million in assistance for Cambodia’s military.
Closer military ties work for both sides. They provide Cambodia’s armed forces with the ability to shore up its security, and give China a strong regional partner that supports key Chinese initiatives and positions from Taiwan to the South China Sea.
Earlier in the year, China and Cambodia kicked off a military exercise dubbed “Golden Dragon.” It focused on counterterrorism and rescue operations, highlighting the strong ties between the two countries. The cooperative effort seemed to highlight the strained relationship between Cambodia and the United States.
Last year, Cambodia suspended a planned joint military exercise with the U.S. Army, “Angkor Sentinel,” which was going into its eighth year. Also canceled was a long-running U.S. Navy program that provided humanitarian assistance in the country. Cambodia said its forces were too busy to join the annual exercise.
A sign of the times?
More worrisome to many Cambodians is the number of Chinese now living in areas of Phnom Penh and Cambodia’s coastal province, Preah Sihanouk.
| By the numbers | National |
|---|
Sihanoukville, once a sleepy coastal town popular with backpackers, is now dominated by Chinese workers, Chinese developers and Chinese-funded projects — such as casinos catering to Chinese tourists. Many Cambodians see the onslaught of Chinese as a threat to their safety, suggesting the Chinese-run hotels, restaurants, casinos and karaoke bars over the past five years are connected to increased crime. Hun Sen has tried to quell the rising fear, saying criticism of Chinese influence is “ignorant” and most of the Chinese arrivals to Cambodia are tourists who do not stay in the country. But 27-year-old tuk-tuk driver Sok Ny disagrees. Waiting for his clients near Phnom Penh’s biggest casino, NAGA World, Sok Ny told VOA Khmer that he worries about the influx of Chinese.
“There are too many Chinese now, Sihanoukville is an example. They cause lots of chaos trouble,” said Sok Ny, who spent more than four years driving a bus for Chinese tourists. He didn’t like it when they drank on the bus or “brought girls in.”
Sok Ny used his savings to purchase a tuk-tuk, only to find himself still ferrying Chinese clients around town.
“I don’t feel comfortable when they sit behind me, I often glance at them in the rear mirrors,” Sok Ny said.
But his biggest concern is not back-seat parties. Sok Ny objects to a concession of 40,000 hectares of land in Koh Kong Province.
“There are too many Chinese in Cambodia, and now the Koh Sdach area is occupied by a Chinese company. I am worried that our territory is being given to China.”

“There are too many Chinese in Cambodia, and now the Koh Sdach area is occupied by a Chinese company. I am worried that our territory is being given to China.”
Dara Sakor Beach at Botum Sakor in Cambodia’s Koh Kong province is part of a Cambodian government land concession made to Chinese interests. (Samrang Pring | Reuters)
The source of Sok Ny’s outrage is a 2008 Cambodian government grant to Chinese company, Union Development Group (UGD). A $4 billion development with a 99-year lease on a vast swath of land within the previously protected Botumsakor National Park was envisioned to include hotels, a casino, a golf course and a seaport on pristine coastal lands, according to the building plans. Thousands of people were evicted from their homes in exchange for puny compensation packages.
Ten years later, the protests continue.
In January, Yun Min, governor of Preah Sihanouk province, sent a report to the Ministry of the Interior linking Chinese arrivals to a rise in crime. In the report, he stated that of the 6,345 foreigners who requested work permits in the province in 2017, 4,498 were Chinese. The governor’s report, which was leaked to the local media, cited noisy casino patrons, loud clubs and unlicensed Chinese drivers as sources of concern. And, he added, local business owners were upset Chinese-owned businesses were cutting into their profits. All in all, he pointed out more than 10 “negatives” associated with the Chinese, including a rise in “mafia” activity.
Author Strangio told VOA Khmer that the fast pace of growth in Sihanoukville was a “symbol of the intimate relations between the two countries.” However, he added, “it seems that Cambodia is fast moving towards an unhealthy degree of economic and political dependency on Beijing.”